The perished civilisation of the Mayas was more numerous than it was assumed based on known archaeological discoveries. They used a system of watering and drainage of soil that could maintain millions of people. Scientists from Comenius University along with an international team revealed the principles of Mayan agriculture.
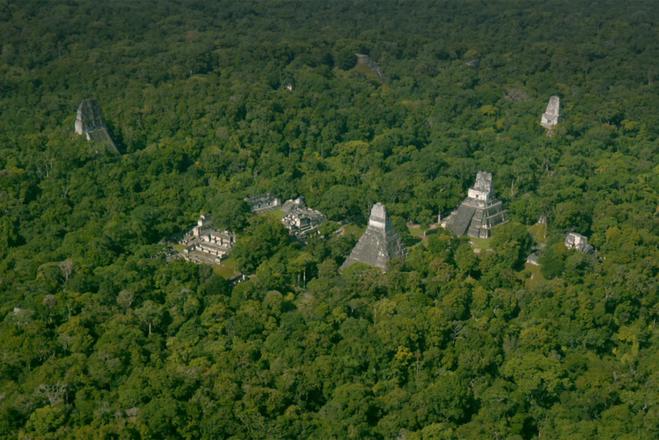
The Mayan civilisation was on the Yucatan peninsula from 1000 BC to 1500 AD. The Mayas are well-known due to their system of writing, art, architecture, astronomy and findings in mathematics. Many aspects of this society were unknown because there are dense primeval forests today in the area where they used to live.
“An international team consisting of scientists from the US, France and Slovakia started to research the primeval forests via laser air scan that penetrates under impervious forest surface in 2016,” said Lenka Miller from marketing department of Comenius University.
Scientists could identify covered cities, palaces and pyramids and other archaeologically interesting objects from the photos, Miller added. They mapped 2,144 square kilometres of Mayan civilisation in Guatemala and identified 61,450 objects.
“We estimated that in the late classical period there lived seven to 11 million people here,” said Miller. This huge population required intense work with soil. The research of agricultural principles was one separate analytic topic of the Slovak team led by Milan Kováč.
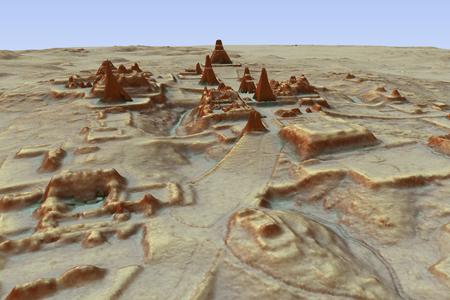
The research revealed a system of watering terrace fields in mountain areas and drainage of swamps in lowlands.
“We were able to identify 5,112 new Mayan constructions from the area we processed separately and 6,080 agricultural terraces in addition,” said Kováč. “We processed and verified the results using archaeological research in terrain. We succeeded in interpreting the results within a social and historical context at an expert level while those results are among the most important parts of collective research since they prove sophisticated agricultural systems.”
The existence of these systems help to clarify high density of population in area and scientists think it can help to understand the so-called “collapse of Mayan civilization” that happened in the 9th century. It also indicates the environmental vulnerability of the system – the destruction of a watering and drainage system that may have led to a lack of food and wars followed by the civilization's demise.


 (source: Comenius University)
(source: Comenius University)